An Interdisciplinary Approach to Study the Performance of Second-generation Genetically Modified Crops in Field Trials: A Case Study With Soybean and Wheat Carrying the Sunflower HaHB4 Transcription Factor.
Autores: González, F. G., Rigalli, N., Miranda, P. V., Romagnoli, M., Ribichich, K. F., Trucco, F., Portapila, M., Otegui, M.E. and Chan, R. L.
Publicado en Frontiers in Plant Science, 11. doi:10.3389/fpls.2020.00178
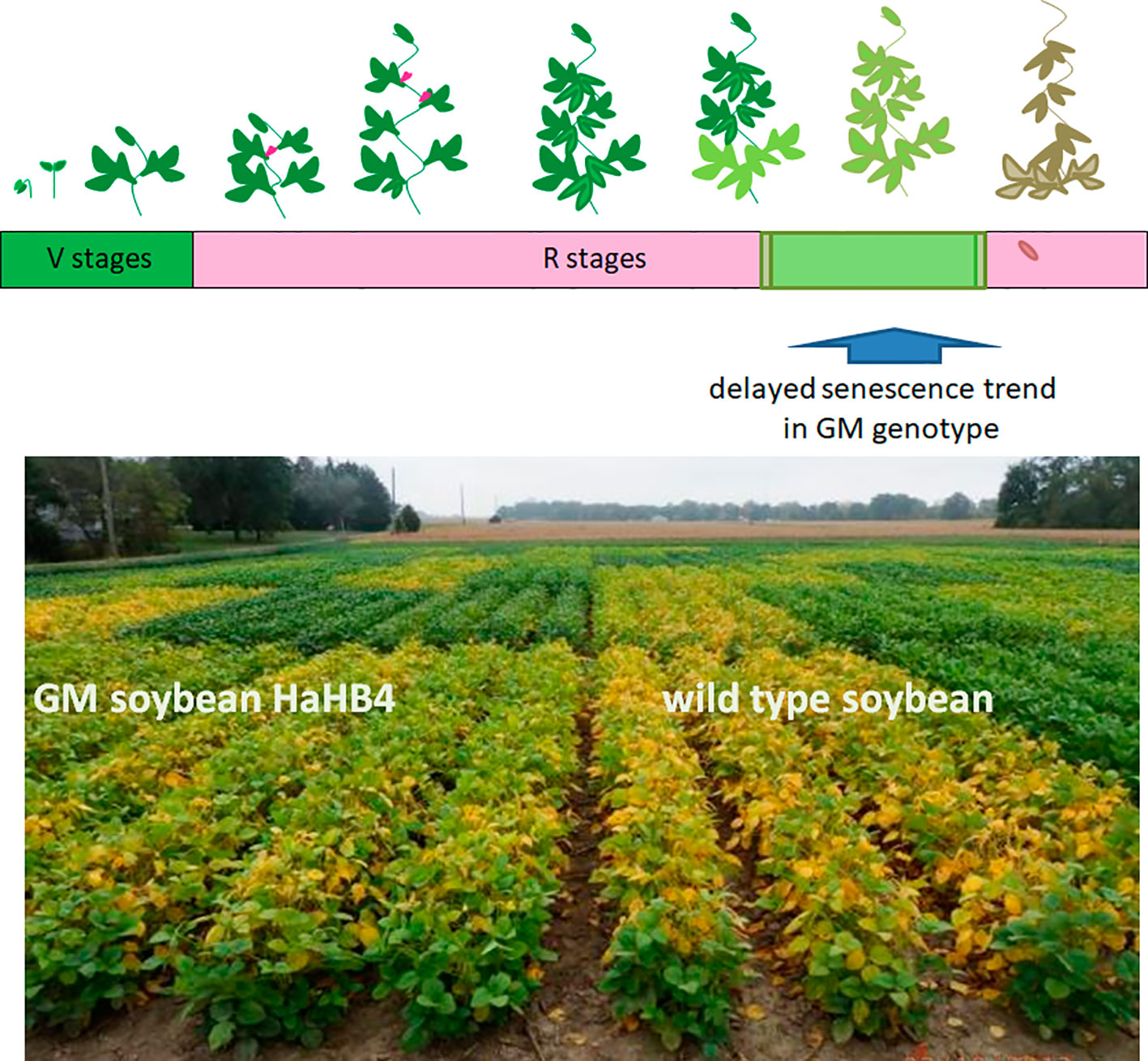
GM soybean exhibits delayed senescence compared with its wild-type control. Upper panel: schematic representation of the soybean life cycle. Lower panel: illustrative picture of one of the field trials performed comparing the wild type genotype (right) with the transgenic HaHB4 one (left).
Successful field performance in dry-warm environments of soybean expressing the sunflower transcription factor HaHB4.
Autores: Ribichich KF, Chiozza M, Avalos-Britez S, Cabello JV, Arce AL, Watson G, Arias C, Portapila M, Trucco F, Otegui ME, Chan RL
Publicado en Journal of Experimental Botany doi: 10.1093/jxb/eraa064
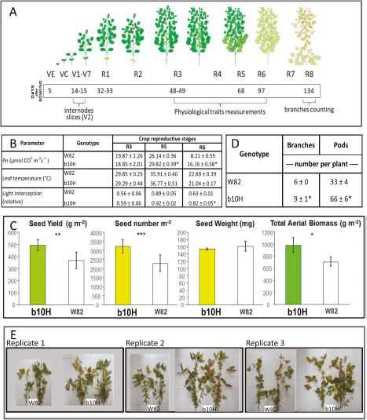
Seed yield components differ between field-grown transgenic b10H and wild-type W82 soybean in the warm and wet environment of the IAL site. (A) Details of assessed characteristics and dates of data collection during the soybean crop cycle in a field trial carried out at the IAL site. (B–D) Comparison between b10H and W82 of (B) physiological traits measured at different growth stages (Pn, net photosynthetic rate), (C) seed yield and yield components, and (D) number of branches and pods per plant. (E) Illustrative pictures of plants collected from all replicates. In (B) and (D), data are mean ±SE and asterisks indicate significant differences between b10H and W82 (P<0.05). In (C), error bars represent SEM×2 and asterisks indicate significant differences between b10H and W82 (*P<0.10, **P<0.05, *** P<0.01).