- Noticias / Improved serodiagnosis of Trypanosoma vivax infections in cattle reveals high infection rates in the livestock regions of Argentina
PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases
Improved serodiagnosis of Trypanosoma vivax infections in cattle reveals high infection rates in the livestock regions of Argentina
Article
Compartir en
redes sociales
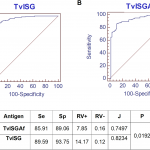
Bovine trypanosomosis, caused by Trypanosoma vivax, currently affects cattle and has a significant economic impact in sub-Saharan Africa and South America. The development of new diagnostic antigens is essential to improve and refine existing methods. Our study evaluated the efficacy of two recombinant antigens in detecting specific antibodies in cattle. These antigens are derivatives of an invariant surface glycoprotein (ISG) from T. vivax. A fraction of a previously described antigen (TvY486_0045500), designated TvISGAf, from an African strain was evaluated, and a new ISG antigen from an American isolate, TvISGAm, was identified. The two antigens were expressed as fusion proteins in Escherichia coli: TvISGAf was fused to the MBP-His-tag, and TvISGAm was obtained as a His-tag fused protein. An ELISA evaluation was conducted using these antigens on 149 positive and 63 negative bovine samples. The diagnostic performance was enhanced by the use of a combination of both antigens (referred to as TvISG-based ELISA), achieving a sensitivity of 89.6% and specificity of 93.8%. Following the validation of the TvISG-based ELISA, the seroprevalence of T. vivax infection in 892 field samples from cattle in the central region of Argentina was determined. The mean seroprevalence of T. vivax was 53%, with variation ranging from 21% to 69% among the six departments studied. These results support the use of the TvISG ELISA as a valuable serological tool for the detection and monitoring of T. vivax infection in cattle. Furthermore, we report for the first time the seroprevalence of T. vivax in Argentina, which highlights the widespread endemic nature of the disease in the region. In order to effectively manage the increasing spread of T. vivax in the vast livestock production areas of South America, it is essential to implement consistent surveillance programs and to adopt preventive strategies.
Results
In silico analysis of sequence encoding for a T. vivax invariant surface glycoprotein and its recombinant expression
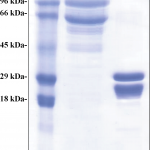
The information available in the database of the T. vivax Y486 genome project database (http://tritrypdb.org/tritrypdb/) contains a 1203 bp open reading frame (TvY486_0045500) that encodes an invariant surface glycoprotein of 400 amino acids with a theoretical molecular mass of 44.5 kDa, S1 Fig, previously analyzed by Fleming et al., 2016 [24]. Based on this information, we searched the genomic data of an American T. vivax isolate [29] for a putative gene encoding an invariant surface glycoprotein. Using the BLASTn tool and the nucleotide sequence of TvY486_0045500, we identified a nucleotide sequence encoding a putative invariant surface glycoprotein (tig00000163, [29]). The amino acid sequence is presented in S2 Fig. In silico analysis predicted that both African and American T. vivax invariant surface glycoproteins have a typical ISG domain structure with an N-terminal signal peptide, a transmembrane domain, and an intracellular domain (S1 and S2 Figs). Amino acid sequence analysis of African and American T. vivax ISG revealed that these proteins share ~63% identity and ~69% similarity (S3 Fig).
Based on previous information [24] and predictions of linear epitopes (S4 Fig), we amplified truncated ISG sequences from African (TvISGAf) and American (TvISGAm) T. vivax genomic DNA by PCR (without the signal peptide and N-terminal transmembrane domain). The resulting DNA sequences were cloned into the pGEM-T Easy vector for analysis. To characterize the antigenic functionality of the recombinant proteins, we first tried sought to express the recombinant antigens (TvISGAf, from amino acid 126 to 400 and TvISGAm, from amino acid 125 to 274) in E. coli as His-tag or N-terminal MBP His-tag fusion proteins using the plasmids pET28 and pMOMAL, respectively. After evaluating the different induction conditions, we were only able to obtain the TvISGAm antigen as an N- and C-terminal double His-tag fusion protein and the TvISGAf as a fusion protein with an N-terminal MBP His-tag. These expression systems allowed us to successfully obtain the overexpression of the recombinant antigens in soluble form. Therefore, we continued the serological evaluations using the recombinant antigens obtained by these two strategies. Similar difficulties with the recombinant expression of the antigen derived from the African strain have been described previously [24]. The amino acid sequences of the recombinant proteins are shown in S5 Fig. SDS-PAGE analysis showed that the recombinant proteins were produced and isolated with high electrophoretic purity (Fig 2). However, a band of lower apparent molecular mass with similar relative abundance was observed in both cases (Fig 2). Co-purification of a truncated product could explain this result, since the purification tags are located towards the N-terminus of the recombinant proteins. The purified recombinant proteins were stored at -80°C for at least 8 months.